This Note contains:
- Agile Method
- Lean Method
- Combination of Scrum and Kanban
- Agile Development
- Lean Development
- Combination of Method
Agile Development
Agile: fast, able to quickly react to change
Agile Methods
- Scrum (used the most)
- Extreme programming (XP)
- Feature-Driven Development (FDD)
- Dynamics System Development Method (DSDM)
- Adaptive Software Development
- Crystal Methods
Agile Manifesto
In agile, We value these:
- Individuals and interactions
- Responding to change
- Customer collaboration
- Working software
More than:
- Processes and tools
- Comprehensive documentation
- Contract negotiation
- Following & plan
Compare to waterfall
The waterfall approach is inverse of the agile, which means the waterfall values Processes and tools, Comprehensive documentation, Contract negotiation and Following & plan more.
Compare to iterative and incremental
As the same as agile, iterative and incremental approach also values Working software and Customer collaboration more. But for Individuals and interactions and Responding to change is not,
In interactive and incremental approach, change is expected but controlled. A change needs to be evaluated against any risks that it might introduce to the project and the team needs to agree that the risks could be mitigated before accepting the change.
In Agile, change is not controlled and always welcome.
In iterative and incremental method, it tend to look at the development team as a machine following a process and overlook the human side of software engineering.
Summary of comparison
- Individuals and interactions (Agile)
- Responding to change (Agile)
- Customer collaboration (Agile, I&I)
- Working software (Agile, I&I)
- Processes and tools (Waterfall, I&I)
- Comprehensive documentation (Waterfall, I&I)
- Contract negotiation (Waterfall)
- Following & plan (Waterfall)
12 Principle
- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through the early and continuous delivery of valuable software .
- Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.
- The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
- Simplicity–the art of maximizing the amount of work not done–is essential.
- The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Scrum
Lifecycle
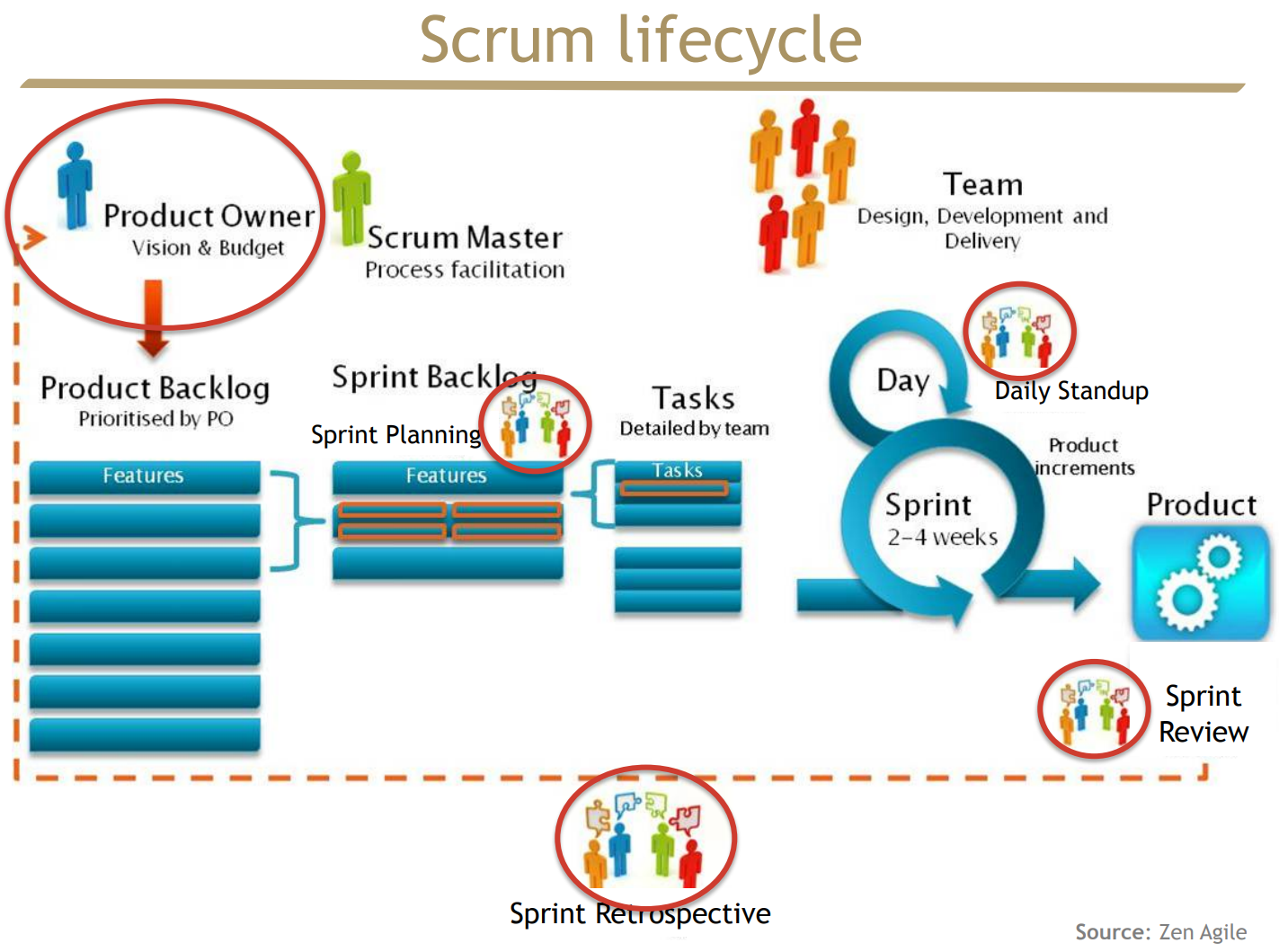
Agile value in Scrum Practice
Customer Collaboration
Principle 4: Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project
This principle could be implemented differently in different methods.
For instance, in XP, it is implemented using the practice of having a real customer available onsite. In Scrum, this is implemented using the practice of having a Product Owner embedded in the team.
- The Product Owner is not the real customer, but he should be working closely with the customer so he can represent the customer.
Responding to change
Principle 2: Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage
This is implemented in Scrum using the practice of continuously updating and prioritizing the Product Backlog.
Product Backlog: It is composed of a number of features to be implemented. These feature are prioritized by the Product Owner based on customer value.
New feature could be proposed by anyone at anytime, and also the backlog could be reprioritized.
Working software
Principle 1: Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through the early and continuous delivery of valuable software .
This principle is implemented in Scrum using the practices of Iterative Development and Sprint Review.
The Scrum lifecycle shows that the project is decomposed into series of iterations, called sprints. Each iteration is 2-4 weeks long, and it focuses on implementing a subset of high value features. Through out the iteration, the team meets everyday during a standup meeting.
In addition, every sprint have a sprint review, to demo the new feature implemented. Audience is the Product Owner and other stakeholders.
Individual and Interaction
Principle 12: At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
It is implemented in Scrum using the practice of Sprint Retrospective.
The entire team holds a retrospective after each sprint. They reflect on what went well/wrong and what to improve during the next sprint.
What is miss in Scrum as a developer?
Scrum is a project management framework, in the sense that it provides some guidance on how to manage the project and organized the teams.
But the scrum does not any guidance on how to perform the technical work.
For this practice, that is where XP comes in handy.
XP (Extreme Programming) technical practices example
- Test first: writing unit test before writing code.
- Pair-programming: 2 developer working on one workstation, learn from each other an improve code quality.
- incremental design: Instead of starting with a complex design that solves many problems, the idea is to start with a simplest design that solves only one problem and then continuously improve the design through refactoring.
Benefits of Agile
- Ability to manage changing priorities
- Increased productivity
- Improved project visibility
- …
Barrier to Agile adoption
- Inability to change organization culture
- General resistance for changing
- Trying to fit agile elements to non-agile framework
- …
Lean Development
For a system, being lean means being optimized in terms of effectiveness, with no waste generation.
Lean Approach
Lean Principles: Applicable to software
Key element: Systems approach to optimize flows and reduce waste.
Lean Principles
There are 5 Principles in lean development approach.
- Identify value
- Make sure you understand what value means from the perspective of your customer
- Map value stream
- Identify all the step of your process, and eliminate the ones that do not create value
- Create flow
- Organize the steps into a continuous flow, from the original idea to delivering value to customer
- Implement pull
- involve the customer in deciding what needs to be built next
- Seek perfection
- Continue the cycle until perfect value is created with no waste
Waste
There are about 7 form of manufactoring waste:
- Inventory
- Over Processing
- Motion & Double handling
- Waiting & Searching
- Overproduction
- Defects & Rework
- Transportation
Lean Method we focused
- Kanban
- Lean Software Development
KanBan
Kanban approach to change:
- First start with the foundation principles
- Then adopt the core practice
Kanban foundational principles:
- Start with what you do now
- Agree to pursue incremental, evolutionary change
- Initially, respect current roles, responsibilities and job titles
Kanban Core Practice
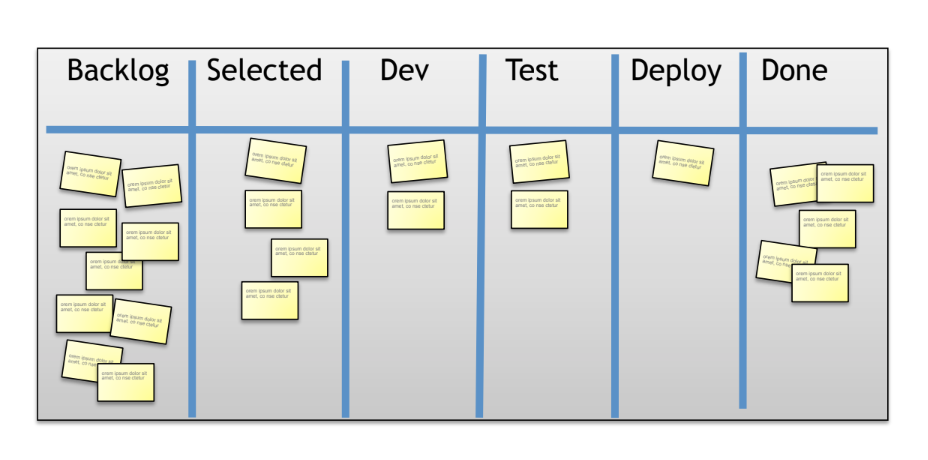
Visualize the workflow
The visualization is done by the Kanban board. In this case, the workflow involves selecting items from a backlog, and a item could be a feature to be implemented for instance. Once select and item, then moves it to development state, to the test state, to the deployment state. Once deployed, the item is to move to done.
Limit WIP (work in progress)
The idea is to assign explicit limits to how many items may be in progress at each development state.
Measure & Optimize flow
What we measure here is the lead time, or the average time that an item spends in the system, from selected to deploy.
Defer commitment
The commitment to implement an item is deferred until the item is selected. Item remain in the backlog might not be implemented.
Benefit of Kanban Practice
The defer commitment can minimize production of unnecessary features.
The implement pull system can make the production based on actual customer demand.
The limit of WIP has benefits on
- Bottleneck identification
- Team Collaboration and learning
- Inventory reduction
- lead time reduction
- Quality improvement
Combination of Method
Scrum vs Kanban
Scrum
- iterative (sprint = iteration)
- requirement: Flow of project-wide activities
Kanban
- Not iterative in the same way as Scrum. More like a conveyer belt or a pipeline with lots parallelism.
- requirement: Flow describing how a piece of requirement is translate to a delivered feature.
3 Question
Team Composition and Roles: How does each approach team composition? What project/team roles does each prescribe?
- Scrum: Advocates cross-functional teams.
- Roles Product Owner
- Development Team
- Scrum Master
- Kanban: Does not say anything about it Roles
- Scrum: Advocates cross-functional teams.
Constraints: What kind of limits does each impose on the process, timing, organization, or workload?
- Scrum:
- 30-day sprints limiting Work-in-Progress within and iteration to sprint backlog
- Work item must fit in a sprint
- Kanban:
- Limits Work-in-Progress per workflow state
- In a workflow state, work item must be compatible with the number of people available to tackle them and how much work they can take on at one time
- Scrum:
Practice: Which regular practices does each prescribe?
- Scrum:
- Product Backlog
- Sprint Planning, Estimation
- Kanban:
- Scrum:
- 本文作者: Depasinre
- 本文链接: https:/Depasinre.github.io/2024/01/23/18652-week2/
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 MIT 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
