This note includes multiple leetcode algorithm problems with my solution
- 1. Reverse String
- 2. Squares of a Sorted Array
- 3. Maximum Average Subarray I
- 4. Check if the Sentence Is Pangram
- 5. Missing Number
- 6. Counting Elements
- 7. Max Consecutive Ones III
- 8. Middle Node Of The Linked List
- 9. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- 10. Running Sum of 1d Array
- 11. Minimum Value to Get Positive Step by Step Sum
- 12. K Radius Subarray Averages
- 13. Subarray Product Less than K
- 14. Intersection Of Multiple Arrays
- 15. Check if All Characters Have Equal Number of Occurrences
- 16. Subarray Sum Equals K
- 17. Count Number of Nice Subarrays
- 18. Find Players With Zero or One Losses
- 19. Largest Unique Number
- 20. Maximum Number of Balloons
1. Reverse String
Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters s.
You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
1 | Input: s = ["h","e","l","l","o"] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: s = ["H","a","n","n","a","h"] |
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105s[i]is a printable ascii character.
My Solution
Use 2 pointer approach
1 | var reverseString = function(s) { |
2. Squares of a Sorted Array
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11] |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in non-decreasing order.
Follow up: Squaring each element and sorting the new array is very trivial, could you find an O(n) solution using a different approach?
My Solution
1 | /** |
Smarter Solution
Intuition
Since the array A is sorted, loosely speaking it has some negative elements with squares in decreasing order, then some non-negative elements with squares in increasing order.
For example, with [-3, -2, -1, 4, 5, 6], we have the negative part [-3, -2, -1] with squares [9, 4, 1], and the positive part [4, 5, 6] with squares [16, 25, 36]. Our strategy is to iterate over the negative part in reverse, and the positive part in the forward direction.
Algorithm
We can use two pointers to read the positive and negative parts of the array - one pointer j in the positive direction, and another i in the negative direction.
Now that we are reading two increasing arrays (the squares of the elements), we can merge these arrays together using a two-pointer technique.
1 | /** |
3. Maximum Average Subarray I
You are given an integer array nums consisting of n elements, and an integer k.
Find a contiguous subarray whose length is equal to k that has the maximum average value and return this value. Any answer with a calculation error less than 10-5 will be accepted.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [1,12,-5,-6,50,3], k = 4 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [5], k = 1 |
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= k <= n <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
My Solution
1 | /** |
More Optimized Solution
The general logic is the same, but the algorithm is optimized in the smallest details.
1 | var findMaxAverage = function(nums, k) { |
4. Check if the Sentence Is Pangram
A pangram is a sentence where every letter of the English alphabet appears at least once.
Given a string sentence containing only lowercase English letters, return true if sentence is a pangram, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
1 | Input: sentence = "thequickbrownfoxjumpsoverthelazydog" |
Example 2:
1 | Input: sentence = "leetcode" |
Constraints:
1 <= sentence.length <= 1000sentenceconsists of lowercase English letters.
My Solution
1 | /** |
More Optimized Solution
Can form a Set with the constructor without the loop (it loop inside but with better optimized and tidy code)
1 | /** |
5. Missing Number
Given an array nums containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only number in the range that is missing from the array.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [3,0,1] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [0,1] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1] |
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1040 <= nums[i] <= n- All the numbers of
numsare unique.
Follow up: Could you implement a solution using only O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) runtime complexity?
My Solution
1 | /** |
Smarter Solution
Calculate the sum based on equation (O(1)), minus the sum of the array
1 | /** |
6. Counting Elements
Given an integer array arr, count how many elements x there are, such that x + 1 is also in arr. If there are duplicates in arr, count them separately.
Example 1:
1 | Input: arr = [1,2,3] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: arr = [1,1,3,3,5,5,7,7] |
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 10000 <= arr[i] <= 1000
My Solution
1 | /** |
7. Max Consecutive Ones III
Given a binary array nums and an integer k, return the maximum number of consecutive 1‘s in the array if you can flip at most k 0‘s.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0], k = 2 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1], k = 3 |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105nums[i]is either0or1.0 <= k <= nums.length
Correcting the understanding of the topic: you can flip at most
kmeans that you can flip an 0 to 1, which not means that swap 2 elements.
My Solution
1 | /** |
核心思想
题目要求找到一个长度最长的子数组,其中最多可以有 k 个 0 被翻转为 1。也就是说,需要找到一个满足条件的最长的子数组, 该数组最多可以包含k个0.
算法步骤
定义滑动窗口:
- 用两个指针
left和right来定义一个窗口,窗口内包含数组的一个子数组。 right用于扩展窗口,left用于收缩窗口,确保窗口内的0的数量不超过k。
- 用两个指针
扩展窗口:
- 开始时,
left和right都指向数组的第一个元素。 - 随着
right的增加,不断地向右扩展窗口,同时检查这个窗口内有多少个0。 - 如果窗口内的
0数量小于k,说明这个窗口是合法的(即最多可以翻转k个0),因此可以继续扩大窗口。
- 开始时,
收缩窗口:
- 当窗口内的
0数量等于k时,继续扩展窗口(right向右移动)。 - 如果在扩展过程中遇到一个新的
0,意味着再继续扩展窗口将导致0的数量超过k,这个窗口就不再合法。 - 为了保持合法性,需要收缩窗口,即移动
left指针,将窗口内的0数量减少到不超过k。
- 当窗口内的
更新最大窗口长度:
- 每次扩展或收缩窗口后,都要计算当前窗口的长度,并与记录的最大窗口长度进行比较,如果当前窗口长度更大,则更新最大窗口长度。
循环直到结束:
- 一直重复上述步骤,直到
right到达数组的末尾。此时,已经找到了能够满足条件的最长子数组。
- 一直重复上述步骤,直到
- 为什么先移动再检查?
在滑动窗口的算法中,先移动指针(右边界
right)再检查0的数量是否合规,是一种贪心策略。这个策略有几个优势:
- 简化实现:通过先移动再检查,我们不需要考虑多种情况(例如下一个
0是否会超过限制),只需要专注于当前窗口是否合法。如果不合法,就通过调整左边界来缩小窗口直到合法。- 动态调整:在窗口扩展的过程中,你随时可以通过缩小窗口来调整,使其重新符合条件。这个策略确保每一步都在一个有效的范围内操作,而不必预先计算或预测未来的情况,这减少了复杂性。
- 时间复杂度的优化:预先检查可能需要额外的计算和判断,使得算法复杂度更高,甚至可能导致一些不必要的计算。而“先移动再检查”的策略确保了每次移动是必要且有效的,避免了重复和冗余的操作。
- 为什么不选择预测下一步是否合规?
虽然从逻辑上看,先预测下一步是否合规再决定是否移动可能显得更加“严谨”,但在实际操作中,这种方法往往会带来复杂的边界情况处理和多余的计算。
- 复杂性增加:如果你尝试在移动之前预先检查是否合规,你需要考虑多种可能的情况,比如下一个元素是否为
0,窗口是否需要缩小,左边界是否也需要调整等。每种情况都可能带来额外的条件判断,增加了代码的复杂性。- 操作冗余:预先预测需要你在每次移动之前都进行一次完整的检查,可能会涉及到重复计算。而这些计算在实际移动后可能并不需要进行,从而浪费了资源。
- 灵活性下降:如果先预测再移动,你需要提前定义好所有可能的操作路径,这种方式在处理一些复杂或特殊情况下可能表现得不如先移动再调整的方法灵活。例如,当窗口中突然出现连续多个
0时,先预测再移动的策略可能需要复杂的判断逻辑来确定如何操作,而先移动再调整的方法则可以自然而然地处理这些情况。
- 为什么“先移动再检查”的策略足够好?
先移动再检查实际上是一种懒惰计算的方式,即仅在需要时才做出调整,而不是提前计算。懒惰计算的好处是它避免了不必要的操作,保持了算法的简单和高效。即使在极端情况下(比如窗口内突然多了很多
0),你仍然可以通过调整左边界来保证窗口的合法性。这种策略可以被视为一种“宽容”的方式,即允许窗口扩展,即使它可能会暂时超出限制,然后通过后续的调整来恢复窗口的合法性。这种方式不仅易于实现,还能保证在最坏情况下的效率。
8. Middle Node Of The Linked List
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
Example 1:

1 | Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] |
Example 2:

1 | Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
My Solution
1 | /** |
9. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
Given the head of a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appears only once. Return the linked list sorted as well.
Example 1:
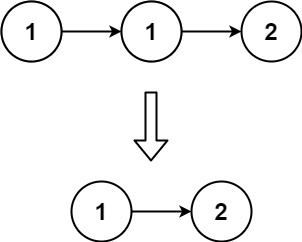
1 | Input: head = [1,1,2] |
Example 2:
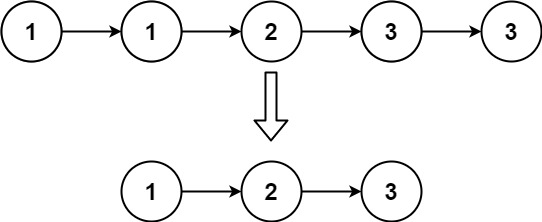
1 | Input: head = [1,1,2,3,3] |
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 300]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100- The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.
My Solution
1 | /** |
10. Running Sum of 1d Array
Given an array nums. We define a running sum of an array as runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i]).
Return the running sum of nums.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [1,2,3,4] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: nums = [3,1,2,10,1] |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000-10^6 <= nums[i] <= 10^6
My Solution
1 | /** |
11. Minimum Value to Get Positive Step by Step Sum
Given an array of integers nums, you start with an initial positive value startValue.
In each iteration, you calculate the step by step sum of startValue plus elements in nums (from left to right).
Return the minimum positive value of startValue such that the step by step sum is never less than 1.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [-3,2,-3,4,2] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [1,2] |
Example 3:
1 | Input: nums = [1,-2,-3] |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100-100 <= nums[i] <= 100
My Solution
1 | /** |
12. K Radius Subarray Averages
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Example 1:
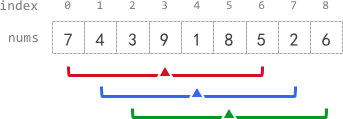
1 | Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 |
Example 3:
1 | Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 |
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
My Solution
1 | /** |
13. Subarray Product Less than K
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k, return the number of contiguous subarrays where the product of all the elements in the subarray is strictly less than k.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [10,5,2,6], k = 100 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [1,2,3], k = 0 |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 1041 <= nums[i] <= 10000 <= k <= 106
My Solution
1 | /** |
关键点: 在这题条件中, 如果我们已经知道一个sub array满足 乘积小于k 的条件, 那么这个sub array的所有 sub array 也一定满足条件 ( 因为规定数组中的整数 >= 1)
14. Intersection Of Multiple Arrays
Given a 2D integer array nums where nums[i] is a non-empty array of distinct positive integers, return the list of integers that are present in each array of nums sorted in *ascending order***.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [[3,1,2,4,5],[1,2,3,4],[3,4,5,6]] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]] |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10001 <= sum(nums[i].length) <= 10001 <= nums[i][j] <= 1000- All the values of
nums[i]are unique.
My Solution
1 | /** |
15. Check if All Characters Have Equal Number of Occurrences
Given a string s, return true if s is a good string, or false otherwise.
A string s is good if all the characters that appear in s have the same number of occurrences (i.e., the same frequency).
Example 1:
1 | Input: s = "abacbc" |
Example 2:
1 | Input: s = "aaabb" |
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000sconsists of lowercase English letters.
My Solution
1 | /** |
16. Subarray Sum Equals K
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k, return the total number of subarrays whose sum equals to k.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [1,1,1], k = 2 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [1,2,3], k = 3 |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000-107 <= k <= 107
My Solution
1 | /** |
This solution is efficiency on memory/space, but inefficiency on time.
Time Efficiency Solution
1 | var subarraySum = function(nums, k) { |
我们使用前缀和的主要目的是将子数组和问题转化为前缀和的差问题。前缀和的定义是:从数组开头到当前位置的元素的和。在数组中找到一个子数组的和等于 k,相当于找到两个前缀和的差值等于 k。
公式上:
- 如果
prefixSum[right] - prefixSum[left - 1] = k,那么nums[left...right]这个子数组的和就是k。 - 通过变换公式,我们有
prefixSum[left - 1] = prefixSum[right] - k。
因此,算法的核心是:
- 遍历数组,累加当前的前缀和
currentSum。 - 检查是否存在一个前缀和等于
currentSum - k。如果存在,说明我们找到了一个子数组的和等于k。
17. Count Number of Nice Subarrays
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k. A continuous subarray is called nice if there are k odd numbers on it.
Return the number of nice sub-arrays.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [1,1,2,1,1], k = 3 |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [2,4,6], k = 1 |
Example 3:
1 | Input: nums = [2,2,2,1,2,2,1,2,2,2], k = 2 |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 500001 <= nums[i] <= 10^51 <= k <= nums.length
My Solution
1 | /** |
18. Find Players With Zero or One Losses
You are given an integer array matches where matches[i] = [winneri, loseri] indicates that the player winneri defeated player loseri in a match.
Return a list answer of size 2 where:
answer[0]is a list of all players that have not lost any matches.answer[1]is a list of all players that have lost exactly one match.
The values in the two lists should be returned in increasing order.
Note:
- You should only consider the players that have played at least one match.
- The testcases will be generated such that no two matches will have the same outcome.
Example 1:
1 | Input: matches = [[1,3],[2,3],[3,6],[5,6],[5,7],[4,5],[4,8],[4,9],[10,4],[10,9]] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: matches = [[2,3],[1,3],[5,4],[6,4]] |
Constraints:
1 <= matches.length <= 105matches[i].length == 21 <= winneri, loseri <= 105winneri != loseri- All
matches[i]are unique.
My Solution
1 | /** |
19. Largest Unique Number
Given an integer array nums, return the largest integer that only occurs once. If no integer occurs once, return -1.
Example 1:
1 | Input: nums = [5,7,3,9,4,9,8,3,1] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: nums = [9,9,8,8] |
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 20000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
My Solution
1 | /** |
20. Maximum Number of Balloons
Given a string text, you want to use the characters of text to form as many instances of the word “balloon” as possible.
You can use each character in text at most once. Return the maximum number of instances that can be formed.
Example 1:
1 | Input: text = "nlaebolko" |
Example 2:
1 | Input: text = "loonbalxballpoon" |
Example 3:
1 | Input: text = "leetcode" |
Constraints:
1 <= text.length <= 104textconsists of lower case English letters only.
My Solution
1 | /** |
- 本文作者: Depasinre
- 本文链接: https:/Depasinre.github.io/2024/09/19/LeetCode-学习-1/
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 MIT 许可协议。转载请注明出处!


